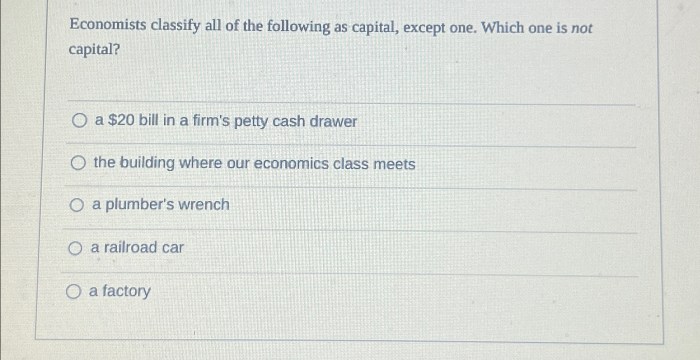
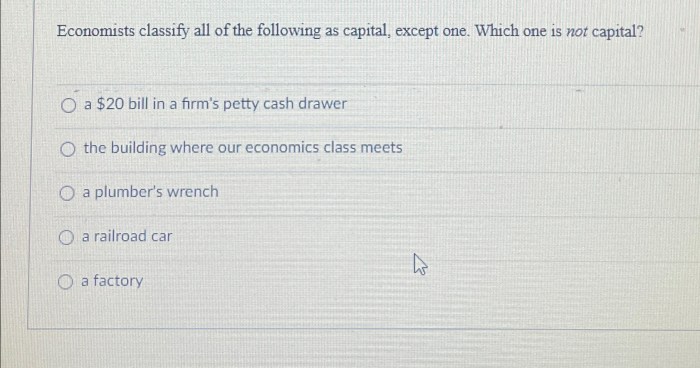
Economists would classify all of the following as land except – Economists classify all of the following as land except, delving into the intricate world of economic factors and their distinct characteristics. Land, as a fundamental factor of production, stands apart from other resources due to its unique attributes and profound economic significance.
This exploration unveils the nature of land, its classification, and its multifaceted role in shaping economic development and sustainability.
Definition of Land
In economics, land is a natural resource that includes the surface of the Earth, its minerals, and its water bodies. It is one of the four factors of production, along with labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Characteristics of Land
Land has unique characteristics that distinguish it from other factors of production. First, it is fixed in supply. The amount of land available for use is limited and cannot be increased.
Second, land is immobile. It cannot be moved from one location to another. This immobility has important implications for the use and development of land.
Examples of Land and Non-Land

| Examples of Land | Examples of Non-Land | Explanation of Land | Explanation of Non-Land |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Ideas | The physical surface of the Earth | Intangible concepts |
| Minerals | Labor | Natural resources found in the Earth | Human effort used in production |
| Water bodies | Capital | Lakes, rivers, and oceans | Man-made resources used in production |
| Forestry | Entrepreneurship | Natural vegetation | Risk-taking and innovation |
Economic Significance of Land: Economists Would Classify All Of The Following As Land Except
Land is a critical factor in economic development. It provides the space for agriculture, industry, and other economic activities. The availability of land can also impact economic growth and sustainability.
Land Classification
Economists classify land in different ways. One common classification system is based on the use of land:
- Agricultural land
- Industrial land
- Residential land
- Commercial land
Another classification system is based on the ownership of land:
- Public land
- Private land
- Common land
Land Use and Planning
Land use planning is the process of managing land resources to meet the needs of society. It involves making decisions about how land will be used for different purposes, such as agriculture, housing, and industry.
Land use planning is important because it can help to ensure that land is used efficiently and sustainably. It can also help to protect the environment and promote economic development.
Land Value and Appreciation
The value of land is determined by a number of factors, including its location, size, and quality. Land value can also appreciate over time due to factors such as population growth and economic development.
Land appreciation can have a significant impact on economic growth. It can increase the wealth of landowners and encourage investment in land.
Land Markets and Regulations
Land markets are the markets in which land is bought and sold. Land markets are typically regulated by government policies, which can impact the price and availability of land.
Government regulations can also affect the use of land. For example, zoning laws can restrict the types of activities that can take place on a particular piece of land.
Top FAQs
What is the definition of land in economics?
In economics, land refers to all natural resources that are fixed in location and cannot be artificially reproduced, including soil, water, minerals, and vegetation.
How is land classified as a factor of production?
Land is classified as a factor of production because it is a natural resource that is essential for the production of goods and services.
What are the unique characteristics of land that distinguish it from other factors of production?
Land is unique in that it is immobile, meaning it cannot be moved or relocated, and its supply is fixed.