Covalent compounds worksheet answer key – Embarking on a journey into the realm of covalent compounds, this comprehensive worksheet answer key unlocks the intricacies of these fascinating chemical entities. Delving into their fundamental concepts, properties, and applications, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for students and educators alike.
Covalent compounds, characterized by the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, exhibit unique properties that distinguish them from ionic compounds. Understanding their nomenclature, reactions, and applications empowers us to appreciate the diverse roles they play in our world.
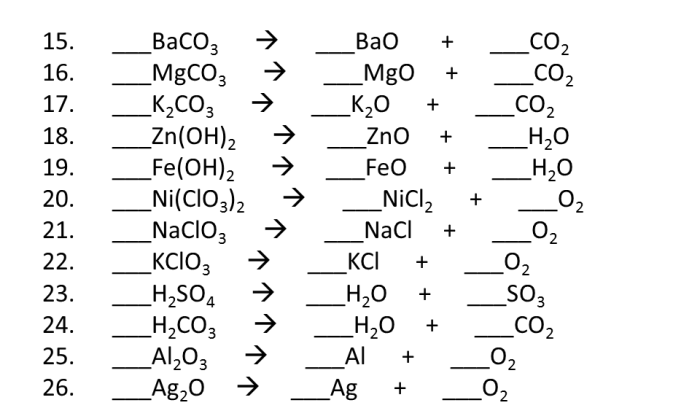
Covalent Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
Answer Key
- Question 1: What is the molecular geometry of CH4?
- Answer: Tetrahedral
- Question 2: What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in CH4?
- Answer: sp3
- Question 3: What is the bond angle in CH4?
- Answer: 109.5°
- Question 4: What is the polarity of the C-H bond in CH4?
- Answer: Nonpolar
- Question 5: What is the molecular geometry of NH3?
- Answer: Trigonal pyramidal
- Question 6: What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in NH3?
- Answer: sp3
- Question 7: What is the bond angle in NH3?
- Answer: 107°
- Question 8: What is the polarity of the N-H bond in NH3?
- Answer: Polar
- Question 9: What is the molecular geometry of H2O?
- Answer: Bent
- Question 10: What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in H2O?
- Answer: sp3
Covalent Compounds Concepts
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. In a covalent bond, the atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, creating a strong attraction between them. Covalent bonds are typically formed between nonmetal atoms.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are two main types of covalent bonds:
- Single bond: A single bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms.
- Double bond: A double bond involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons between two atoms.
- Triple bond: A triple bond involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms.
Examples of Covalent Compounds
Some common examples of covalent compounds include:
- Water (H2O)
- Methane (CH4)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Ethane (C2H6)
Covalent Compounds Properties
Physical Properties
Covalent compounds typically have the following physical properties:
- Low melting points
- Low boiling points
- Low solubility in water
- Low electrical conductivity
Chemical Properties
Covalent compounds typically have the following chemical properties:
- Unreactive
- Flammable
- Nonpolar
Comparison to Ionic Compounds
Covalent compounds differ from ionic compounds in the following ways:
- Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons, while ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons.
- Covalent compounds are typically nonpolar, while ionic compounds are typically polar.
- Covalent compounds have lower melting points and boiling points than ionic compounds.
- Covalent compounds are less soluble in water than ionic compounds.
- Covalent compounds are less reactive than ionic compounds.
Relationship between Properties and Structure
The properties of covalent compounds are related to their structure. For example, the low melting points and boiling points of covalent compounds are due to the weak intermolecular forces between the molecules. The nonpolarity of covalent compounds is due to the equal sharing of electrons between the atoms.
Covalent Compounds Nomenclature
Rules for Naming Covalent Compounds
The following rules are used to name covalent compounds:
- The first element in the compound is named using the root of its element name.
- The second element in the compound is named using the suffix “-ide”.
- The number of atoms of each element in the compound is indicated by a prefix.
Prefixes
The following prefixes are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in a covalent compound:
- mono- (1)
- di- (2)
- tri- (3)
- tetra- (4)
- penta- (5)
- hexa- (6)
Examples of Covalent Compound Names
The following are examples of covalent compound names:
- CH4: methane
- NH3: ammonia
- CO2: carbon dioxide
- C2H6: ethane
Covalent Compounds Reactions
Types of Reactions
Covalent compounds can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Addition reactions: Addition reactions involve the addition of one or more atoms or molecules to a covalent compound.
- Substitution reactions: Substitution reactions involve the replacement of one atom or molecule in a covalent compound with another atom or molecule.
- Elimination reactions: Elimination reactions involve the removal of one or more atoms or molecules from a covalent compound.
Mechanisms of Reactions
The mechanisms of covalent compound reactions vary depending on the type of reaction. However, the following general steps are involved in most covalent compound reactions:
- Initiation: The initiation step involves the formation of a reactive species, such as a free radical or a carbocation.
- Propagation: The propagation step involves the reaction of the reactive species with the covalent compound.
- Termination: The termination step involves the reaction of two reactive species to form a stable product.
Examples of Covalent Compound Reactions
The following are examples of covalent compound reactions:
- Addition of hydrogen to ethene:
- C2H4 + H2 → C2H6
- Substitution of chlorine for hydrogen in methane:
- CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
- Elimination of water from ethanol:
- C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O
Applications of Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds have a wide variety of applications in everyday life. Some of the most common applications include:
- Fuels: Covalent compounds, such as methane and propane, are used as fuels for heating and cooking.
- Plastics: Covalent compounds, such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride, are used to make plastics.
- Solvents: Covalent compounds, such as acetone and benzene, are used as solvents.
- Drugs: Covalent compounds, such as aspirin and penicillin, are used as drugs.
The properties of covalent compounds make them suitable for these applications. For example, the low melting points and boiling points of covalent compounds make them easy to handle and store. The nonpolarity of covalent compounds makes them resistant to water and other polar solvents.
Helpful Answers
What is the difference between covalent and ionic compounds?
Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, while ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
What are the different types of covalent bonds?
Covalent bonds can be classified as single bonds, double bonds, or triple bonds, depending on the number of electron pairs shared between the atoms.
How do you name covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds are named using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule.